Most cacti are without leaves because they transformed themselves to thrive in tropical, desert conditions. The spines of a cactus are supremely customized leaves. The cacti plants are conditioned to survive by preserving water for a longer duration.
During the rains, their broad root system absorbs water efficiently from the soil. If you are amazed at times does a cactus have leaves, actually the leaves of a cactus plant are modified to thorns in order to save the amount of water needed by the plant.
Cacti plants store water for more duration to live in hot arid areas when water is scarce or is not available at all. To grow in hot climates with reserved water, most cacti do not have leaves.
In a leaf, water loss occurs by transpiration from tiny pores called the stomata present on the leaf surface. In hot areas, cactus plants store water in the stems that have a waxy coating to prevent the loss of moisture, and their leaves are transformed into spines. Spines protect the stems from the scorching heat of the sun in deserts. They also protect the cactus plants from animals.
Deserts of North and South America are native places of the cacti plants, but slowly, cacti spread to many areas in the world.
It is very easy to find out the evolution of a cactus in a desert region by analysing it and a plant that lives in humid conditions all over the year. The cactus plants are modified to live in arid conditions by storing water in the stem and using it sparingly.
The cactus being devoid of leaves use their stem to make food, so the loss of water is also prevented in this way.
Cacti lack branches to reduce the area through which water will move. The surface area of the stems in most cacti is reduced by attaining crescent shape and is low in height. In the Mexican deserts, a cactus goes beneath the ground during the dry spell and regenerates after the rains.
The stem of a cactus changes according to the amount of water it stores such as if less water is present in the stem, the stem becomes thin. However, if enough water is stored in the stem, it becomes.
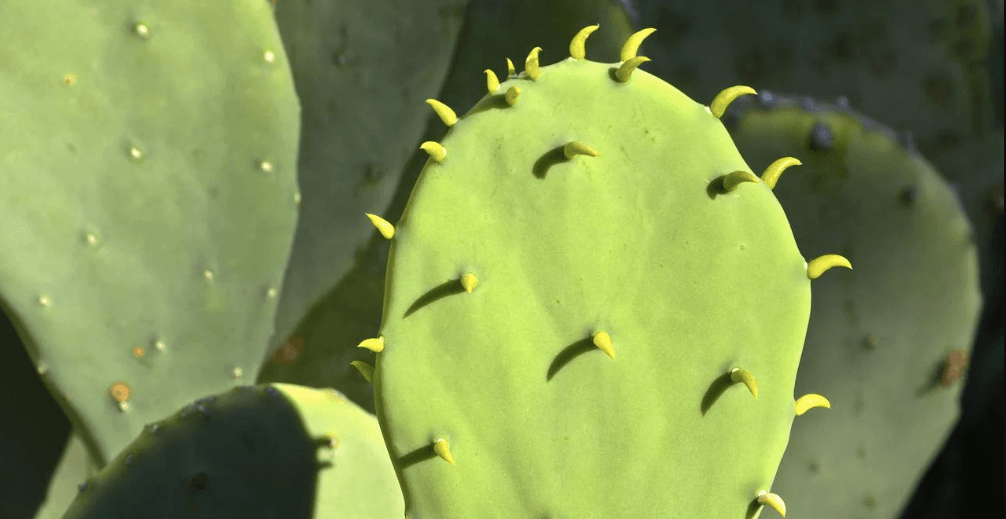

The cacti have thorns to protect themselves from animals. The spines also provide a cover for the plant’s surface, cooling it slightly and minimizing water loss through vaporization.
In some cacti, vaporization is reduced by developing a fluffy substance along with the thorns to envelope a layer of air near the thorns preventing the scorching heat of the Sun to reach the stem.
What Do Cactus Have Instead of Leaves?
Cacti have thorns instead of leaves to avoid a loss of water from the surface of the leaf and also to save water. In most cactus species true leaves or branches are absent.
Rather, they have overly transformed offshoots called areoles – the tiny eruptions from which the spines sprout.
But why are leaves replaced by spines?
One reason for this is since the stem performs photosynthesis in cactus plants and they are usually found in desert regions with ample sunlight.
Reasons For Spines
- Spines capture air: Arid plants mainly focus on minimizing the loss of water. Cactus spines assist plants in retaining water. Cactus spines restrict the airflow around the plant and minimize vaporization by terminating the draft. The draft around the cactus can help provide a somewhat moist neutral zone. This is a great way to retain water.
- They collect water: Cactus spines can help in collecting mist that falls onto the soil closer to the cactus and is taken in by the roots in misty areas. Some fog deserts like Chile and Peru’s Atacama Desert, Mexico’s the Baja California Desert and Namibia’s the Namib Desert have dense fog in the morning that gives the moisture for the growth of various succulents and vegetation. So, even without rain, heavy fog in the morning is gathered by spines as dew for a cactus plant. Remarkable indentations of cactus spines aid in accumulating extra water. Researches are being done to copy this peculiar method of accumulating water in arid areas.
- They give shade: Cactus spines assist cactus plants in saving water by giving shade. Although spines provide little shade, as each cactus plant has numerous spines, the shade given by them really matters. The ridges and indentations of cactus plants also help in providing shade.
- Spines Keep animals away: Cactus spines protect cactus plants from animals who love to eat the flashy part of these succulents due to the water present inside the stem.
Cactus spines have various uses and in general, some cactus species are facing extinction, so we need to do something about it.
Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place in Cactus Plants?
In cactus plants, photosynthesis takes place in the stem of the plant.
The cactus stem has stomata embedded in it to lower the vaporization of water. Various cacti have specific photosynthetic methods.
The saguaro cactus is a big, dendriform, and branched cactus. Photosynthesis is done by the main stem and branches that also preserve water.
Photosynthesis is a process of transforming carbon dioxide gathered through tiny pores called stomata, into glucose and oxygen in the presence of sunlight.
CAM photosynthesis (Crassulacean acid metabolism) is a carbon fixation mechanism developed in certain plants growing in arid conditions in which photosynthesis is done during the day as sunlight is required for it, but exchange of gases occurs only at night.
Cacti use CAM photosynthesis in which stomata open only during the when the temperature is low so that less water vaporization occurs, thereby retaining more moisture.
During CAM photosynthesis, the carbon dioxide is stored till the morning when lots of sunlight is available and, carbon dioxide is utilized for photosynthesis. Stomata are the pores that allow the exchange of air and water in or out, but sunlight can enter in even if stomata are not open.
Cacti are prone to predators’ attack regardless of their spiny covering. Many rats chomp on cactus pads, and fruits of some cacti like Dragon fruit and Prickly pears are relished by certain mammals such as bears and humans. .